GPR119 agonist-mediated PYY release from enteroendocrine Lcells requires glucose and epithelial Y1 receptors
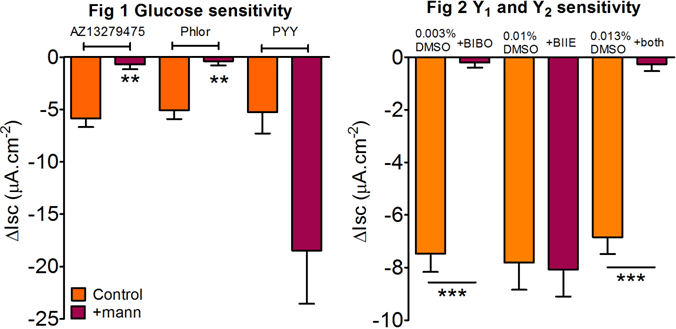
GPR119is a G-protein-coupled receptor thatis located on enteroendocrine L cells, with highest gastrointestinal expression in thedescending colon(1). This receptor is activated by fatty acid ethanolamidesand small-molecule agonists e.g. PSN632408 (2) and results in releaseof glucagon-like peptide (GLP) 1 and 2 and peptide YY (PYY)from L cells (3). PYY slows colonic motility, upper and lower gastrointestinal transit(4) and enhances satiety (5)and thus GPR119 is a potential target for treatment of obesity and type II diabetes. Here we investigated the pharmacology, glucose-sensitivity and peptide mediationof responses to thenovel, selective GPR119 agonist, AZ13279475, in male and female mouse descending colon mucosal sheets (>10 wks; C57BL/6-129/SvJ background). Mucosae were mounted in Ussing chambers,voltage-clamped and the resultant short-circuit current (Isc) was recorded continuously (6) and thenprestimulated with vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (bl; 30nM). Single apical (ap) additions of AZ13279475 (1nM–3μM) reduced the Isc with a pEC50 of 7.3(pEC50 range 8.2-6.4; and a maximal response of -9.3 ± 1.3 μA.cm-2; n=3). AZ13279475 (ap; 100nM) responses in the presence (control) and absenceof glucose (replaced by 11.1 mM mannitol) are shown in Fig.1. In the presence of glucose (ap and basolateral (bl)) AZ13279475 reduced the Isc(-5.9 ± 0.8 μA.cm-2) and this was 88.1 ± 8.0 % attenuated in the presence of mannitol (+mann; ap only; P<0.01; n=4). The responseof the sodium glucose transporter inhibitor, phloridzin (Phlor; ap; 50µM; P<0.01; n=4) was 92.2 ± 7.8% inhibited in the presence of ap mannitol. The PYY (bl; 10nM; P<0.05; n=4) internal control response was glucose-independent (Fig 1). AZ13279475 responses were 97.3 ±2.7% inhibited by the Y1 receptor antagonist, BIBO3304 (BIBO; bl; 300nM; P<0.001; n=4-5) whereas the Y2 antagonist, BIIE0246 (bl; 1μM; n=3) had no effect (Fig. 2). Furthermore, the combination of Y1 and Y2 antagonists (+both) inhibited AZ13279475 responses by 96.1 ± 3.9% (P<0.001; n=3-4).
In conclusion, AZ13279475 stimulatesglucose-sensitive GPR119 receptors causing PYY releasepresumably from L cells. AZ13279475 is a more potent GPR119 agonist compared with PSN632408 (pEC50 of 5.2)and both theirresponsesaremediated viaepithelial Y1 receptors(7). 1. Symonds EL et al. (2015). Gut 64: 618-626 2. Overton HA et al. (2006). Cell Metab 3: 167-1756 3. Lauffer LM et al. (2009). Diabetes 58: 1058-1066 4. Tough IR et al. (2011). Br J Pharmacol 164: 471-478 5. Batterham RL et al. (2006). Cell Metab 4: 223-233 6. Cox HM et al. (2001). Peptides 22: 445-452 7. Cox HM et al. (2010). Cell Metab 11: 532-542 Supported by Astra ZenecaR&D Mölndal, Sweden
|