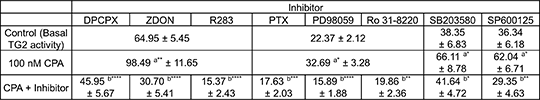
A1 Adenosine Receptor-Induced Modulation Of Transglutaminase 2 Activity In H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts The A1 adenosine receptor (A1R) is a member of the adenosine receptor group of G-protein-coupled receptors, which also includes A2A, A2B and A3. The A1R is Gi/o-protein linked and is involved in neuro- and cardioprotection. Stimulation of this receptor reduces the cardiac infarct size similarly to ischaemic preconditioning as well as activating protein kinases such as PKC, ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK, which have been implicated in cardioprotection (1). Transglutaminase-2 (TG2) is a multifunctional enzyme regulated by Ca2+ and protein kinases (e.g. PKA) and capable of mediating intracellular signalling by acting as a GTP-binding protein (Gαh) (2). TG2 has been implicated in signalling via the α1-adrenergic receptor and in some instances, has been shown to be necessary for cardioprotection (3). The aims of this study are to determine whether TG2 is activated by the A1R the and if so, which protein kinase(s) are involved. Mitotic rat H9c2 cardiomyoblasts were subjected to the selective A1R agonist N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) and TG2 activity measured in vitro (4) and in-situ (5). H9c2 cells were pre-treated with the selective A1R antagonist DPCPX (1 µM: 30 min), Gi/o protein inactivating pertussis toxin (100 ng/ml-1:16h) or TG2 inhibitors Z-DON (150 µM: 60min) and R283 (200 µM: 60min). Where indicated, cells were also treated with the protein kinase inhibitors Ro 31-8220 (PKC inhibitor, 10 µM), PD 98059 (MEK1/2 inhibitor, 50 µM), SP 600125 (JNK1/2 inhibitor, 20 µM) and SB 203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor, 20 µM) for 30 min prior to stimulation with CPA (100nM for 10 min). Results represent mean ± S.E.M. and p values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. CPA (control TG2 activity 30.71 ± 2.48 vs CPA-induced 72.30 ± 1.65; n=6) produced transient increases in TG2-catalysed biotin-cadaverine incorporation activity, peaking at 10 min. Furthermore, CPA (p[EC50] = 8.87 ± 0.17; n=6) stimulated a concentration-dependent increase in amine incorporation activity. Responses to CPA-induced TG2 activity were blocked by the application of the above mentioned inhibitors (Table 1).
Table 1: Effects of inhibitors on CPA-induced TG2 activity.
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001, (a) versus control and (b) versus 100 nM CPA alone. Data obtained from four independent experiments.
In summary, these findings have shown for the first time that the A1R regulates TG2 activity via PKC and a range of protein kinase pathways. 1. Thornton et al. (1992). Circulation 85: 659–665. 2. Eckert R et al. (2014). Physiol Rev 94: 383–417. 3. Gundemir S et al. (2012). Biochim Biophys Acta 1823: 406–419. 4. Slaughter TF et al. (1992). Anal Biochem 205: 166–171. 5. Perry MJ et al. (1995). Neuroscience 65: 1063–1076.
|