| 023P London, UK Pharmacology 2016 |
Prescription analysis, switch overs and quality of life assessment of patients on antipsychotics at a tertiary care hospital: a prospective, observational study
Introduction: The present study aims to analyze antipsychotic prescriptions1, identify the technique and reasons behind switching over from one antipsychotic to another.2 Assessment of quality of life was done to examine the outcome with antipsychotic therapy to better understand the impact of these drugs on health outcome.3
Method: The study, prospective and observational in design, was conducted in the psychiatry outpatients department of a tertiary care hospital in Delhi for 1 year. A total of 224 patients enrolled were followed up for a period of 90 days. WHO core prescribing indicators were assessed. Technique of switching over from one antipsychotic to another was monitored. A subgroup analysis comprising 140 patients was done to assess quality of life using WHO-QOL BREF. The study was conducted as per WHO drug utilization study guidelines and STROBE guidelines.
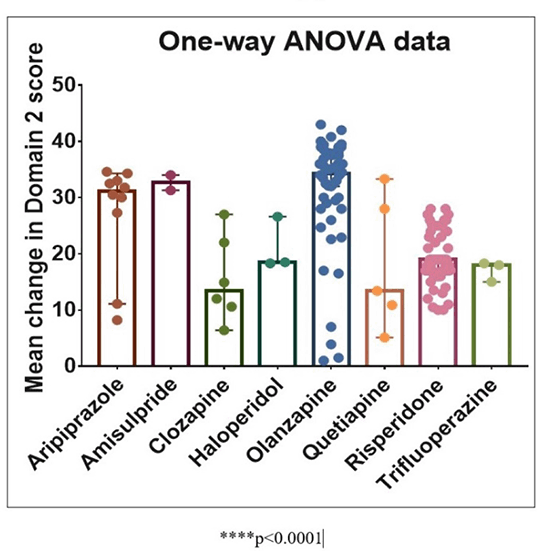
Results: A total of 293 antipsychotics were prescribed over the 90 day study period, of which 88.7% belonged to atypical class (Figure 1). We report 52 patients who switched over from one antipsychotic to another once during the study period while 3 patients switched over twice, thus amounting to total of 58 switches (Figure 2). Significant improvements were noted at 3 months on all four domains; physical, psychological, social and environmental, compared to baseline. A comparison between antipsychotics revealed olanzapine performing better than clozapine, risperidone, and trifluoperazine on physical domain scores (Figure 3). Similarly, olanzapine scores were better compared to risperidone, and clozapine on psychological domain scores (Figure 4).
Conclusions: The study provides information on the existing pattern in the setup. Early switching over could be related to adverse effect while switch over later on in therapy could raise questions on efficacy of the drug. Few antipsychotics performed better on the QOL scale used in the study suggesting that prescription of such antipsychotics would be rational, cost effective and meaningful.
References:
1) Introduction to Drug Utilization Research [Internet]. Apps.who.int. 2014 [cited 27 April 2016].
2) Lambert TJ. (2007). J Clin Psychiatry 68(Suppl 6): 10-13.
3) World Health Organisation. Quality of life WHOQOL-BREF. Switzerland; 2004.
FIGURE 1: Total antipsychotic prescribed during study period
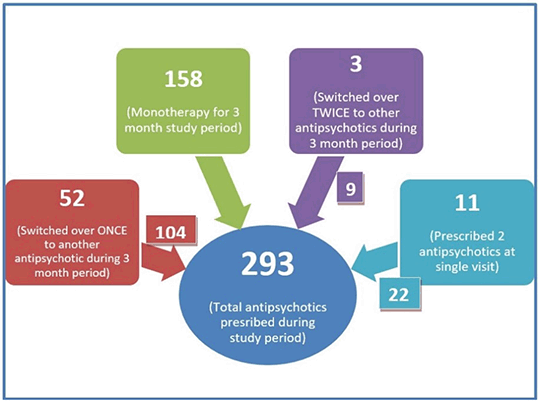
Figure 2: Distribution and type of switch between antispychotics over 12 week period
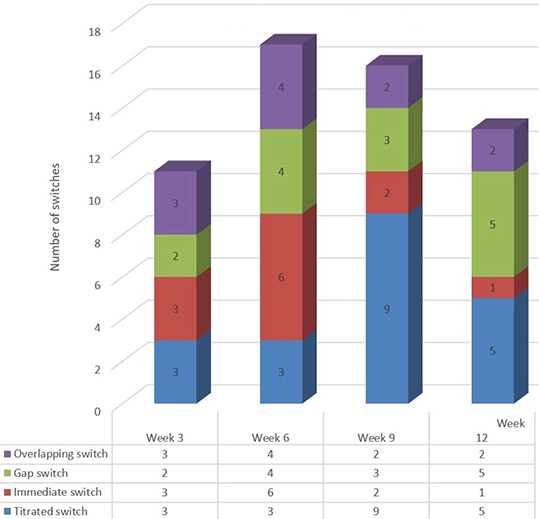
FIGURE 3: Physical domain (Domain 1) score change from baseline to 3 months with various antipsychotics
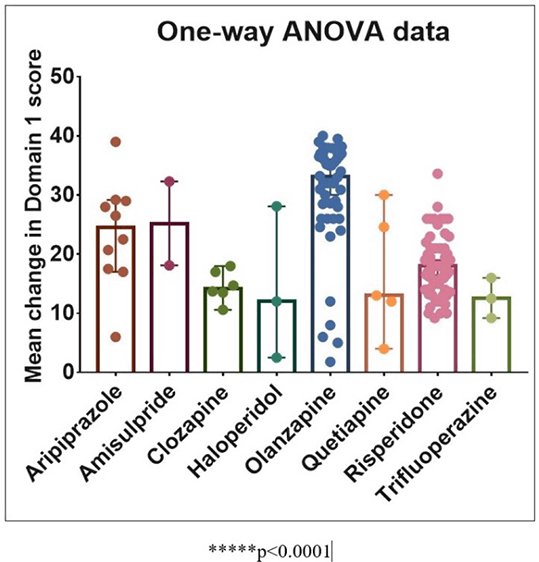
FIGURE 4: Psychological domain (Domain 2) score change from baseline to 3 monts with various antipsychotics