| 128P London, UK Pharmacology 2016 |
The neoflavonoid latifolin isolated from dalbergia odorifera attenuates hypoxia and reoxygenation injury by reactive oxygen species scavenging and nrf2 activation in h9c2 cardiomyocyte
Introduction: Latifolin, as a major neoflavonoid component isolated fromthe heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen, possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, vasodilatory properties, etc1. This study aimed to investigate the effects of latifolinon the hypoxia and reoxygenation(H/R) injury in H9c2 and the possible molecular mechanisms by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2)/antioxidant response element (ARE) pathway2.
Method: H9c2 cardiomyocytes pretreated with latifolin were exposed to hypoxia and reoxygenation (H/R). Cell viability and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity in culture medium were determined by MTT and microcolorimetry. The expression and level of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured by DCFH-DA staining and flow cytometry. The expression and location of Nrf2 were identified by Immunocytochemistry. The expression of Nrf2 and HO-1weredetectedby western blotting. Data are given as mean±SD and analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA.
Results:The results showed that latifolin increased the cell viability, reduced LDH activity (Fig.1)and ROS production(Fig.2). Immunocytochemistry and western blotting analysis showed that latifolin increased the expression of HO-1 in cytoplasm and Nrf2 both in cytoplasm and nuclear(Fig.3).
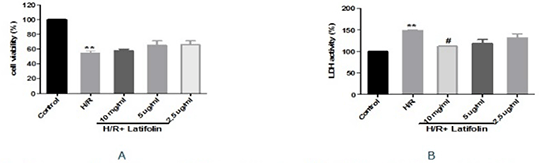
Fig. 1 Effect of latifolin on cell viability and LDH activity. A. cell viability; B. LDH activity. Data were presented as mean ± SD. n=3 per group. *P<0.05, **P< 0.01 vs. control group; #P< 0.05, ##P< 0.01 vs. H/R group.
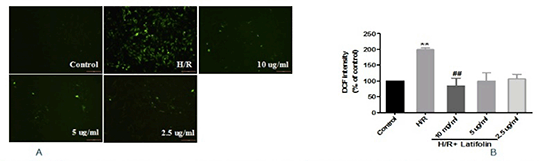
Fig.2 Effect of latifolin on ROS generation. A. Representative photomicrographs for ROS production as assessed by DCFH-DA staining. B.Intracellular ROS levels were determined by flow cytometry. Data were presented as mean ± SD. n=5 per group. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. control group; #P< 0.05, ##P< 0.01 vs. H/R group.

Fig. 3 Western blotting analysis of Nrf2 and HO-1 expression. A. Expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 in cytoplasm. B. Expression of Nrf2 in nucleus.
Conclusion: Pretreatment with latifolin attenuated the cell injury,increased the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1.These findings indicated that the anti-oxidative and ROS scavenging activity of latifolin attenuated H/R injurywhich was related to activating Nrf2/ ARE pathway.
References:
1.Yu X, et al. (2007). Food Chem 104: 715-720.
2. Holly K, et al. (2013). Biochemical Pharmacology 85:705-717.

