| 139P London, UK Pharmacology 2016 |
Polyunsaturated fatty acid ethanolamide activation of CB1 cannabinoid and TRPV1 receptors
Introduction: Probably the most investigated N-acylethanolamine (NAE) is anandamide (AEA, C20:4,ω-6), a weak, partial agonist at CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. AEA also acts as an endovanilloid through activating the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1(TRPV1) ion channel1. We have investigated the actions of a series of NAE analogues, particularly polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) derivatives, as agonists at CB1 and TRPV1 receptors.
Method: A series of NAEs were examined at 10 µM, where TRPV1 activation was measured in rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG)2, while human CB1 receptor activation was studied in Chinese hamster ovary cells3 (n=6).
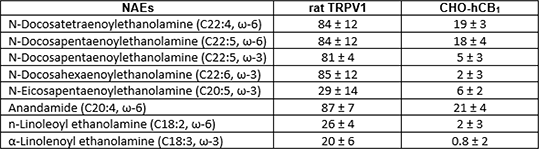
Results: The PUFA NAEs were able to elicit calcium responses in DRGs, to a level similar to the capsaicin response, 85% for N- docohexanoylethanolamine (C22:6, ω-3), 81% and 84% for N-docosapentaenoylethanolamine C22:5, ω-3, C22:5, ω-6 respectively of the response to 10 µM capsaicin, while monounsaturated and saturated NAEs failed to elicit responses at the same concentration (see Table 1). In CHO-CB1 cells, HU210 evoked a rapid phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) to levels of 213 % control. The majority of NAEs failed to elicit a significant change in ERK activation (including C20:0, C18:0; C18:1, ω-9; C22:1, ω-9 and C24:1, ω-9). AEA and NAEs as C22:5, ω-6 and C22:4, ω-6 elicited responses of a similar magnitude to HU210. NAEs C22:5, ω-6 and C22:4, ω-6 evoked similar intracellular calcium responses for AEA (18, 19 vs.21%, respectively of the response to 10 µM ATP) (see Table 1). The majority of NAEs (including C20:0, C18:0; C18:1, ω-9; C22:1, ω-9 and C24:1, ω-9) failed to elicit a significant change in [Ca2+]i in CHO-CB1 cells. The ERK and calcium responses in CHO-CB1 cells were blocked by 100nM AM251 (a selective CB1 antagonist), while pertussis toxin (500ng/ml) blocked ERK responses in these cells.
Conclusion: At both CB1 and TRPV1 receptors, PUFA NAEs evoke greater responses than their mono-unsaturated and saturated counterparts. Long chain ω-3 NAEs responses in DRG neurons highlight the differences in ligands recognition properties between TRPV1 and CB1 receptors
References:1. Alexander SPH and Kendall DA (2007). Br J Pharmacol 152: 602-623.2. Sagar DR et al. (2004). Eur J Neurosci 20: 175-184.3. Priestley RS et al (2015). FASEB J 29: 1446-55.Table1: Intracellular calcium levels in response to NAEs in DRGs neurons and CHO-hCB1. The data are expressed to a % control (ATP for CHO and capsaicin for DRG neuron)