| 214P London, UK Pharmacology 2016 |
Characterisation of lipidated probes using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
Introduction: The neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R), a mediator of pain and inflammation, is activated by the neuropeptide Substance P, resulting in internalisation into endosomes and sustained intracellular signalling [1].
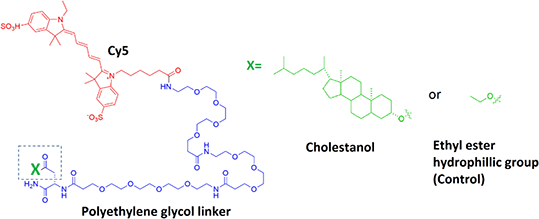
Purpose: Previously it has been demonstrated that lipidation can promote internalisation of a fluorescent probe into endosomal compartments [2]. We aim to investigate lipidation as an approach for the delivery of an NK1R antagonist to target intracellular signalling of the NK1R. Here we have used fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) to determine the actual concentration of lipidated Cy5, Cy5-Cholestanol (Cy5) and a control compound in the vicinity of their target.
Methodology: Cy5-Chol and control compound Cy5-ethyl ester (Cy5-EE), were prepared (5-50nM) in HBSS in the presence or absence of 0.1% BSA. FCS measurements were performed on a Zeiss LSM510 Confocor 3 [3] using 633nm excitation and emission collected through an LP650 filter. The detection volume was positioned 2-200µm above the coverslip and 20 second measurements were recorded. The autocorrelation data analysis was performed as previously described [3] and presented as mean±s.e.mean of ‘n’ independent experiments.
Results: Cy5-Chol and Cy5-EE (added as 10nM without BSA) was measured 200μm above the coverslip, giving concentrations of 0.6±0.1nM and 3.1±0.7nM, respectively (n=4). These increased to 5.9±0.7nM and 9.2±1nM (for Cy5-Chol and Cy5-EE respectively; n=3) in the presence of BSA. There was a linear relationship between the nominal and measured concentration without BSA yielding slopes of 0.06±0.0nM (Cy5-Chol) and 0.22±0.03nM, (Cy5-EE) (R2=0.94 and 0.81; respectively, n=4). In the presence of BSA, slopes increased to 0.46±0.04nM, and 0.94±0.07nM, for Cy5-Chol and Cy5-EE (R2=0.93 and 0.95, respectively; n=3). In contrast, as the distance from the coverslip decreased, the measured concentration increased. At 2µm from the coverslip, with a nominal concentration of 5 nM, prepared without BSA, the detected concentrations of Cy5-Chol and Cy5-EE were 34±5.9nM and 67±28nM (n=3).
Conclusions: Our results indicate loss of both ligands from the bulk buffer due to non-specific binding. The deviation from the nominal concentration was greater for Cy5-Chol which is likely to bind to membranes. This information provides insight into the actual concentrations used in assays with the Cy5 reporter and NK1R antagonist.
References:
[1] Cattaruzza F et al. (2013) Bioschemical Society Transactions 41: 137-43.
[2] Rajendran L et al. (2008). Science 320: 520–3
[3] Ayling LJ et al. (2012). Journal of Cell Science 125: 869-886.