| 020P London, UK 8th European Workshop on Cannabinoid Research |
Effect of RVD-hemopressin on amyloid-β induced toxicity in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells
Introduction: Previous in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the protective properties of lipid endocannabinoids against amyloid-β (Aβ) induced neurotoxicity1,2. Lipid-derived endocannabinoid agonists such as 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) can exert their effects via both the extra- and intracellular cannabinoid receptor-1 (CB1)3. Pepcans are a group of haemoglobin derived peptide cannabinoids and are found throughout the CNS3. They are cell-impermeant and act on the extracellular CB1 receptor3,4 as agonists/antagonists. The pepcan RVD-hemopressin (RVD) is a CB1 receptor agonist3. The aim of this study was to determine whether RVD is protective against Aβ toxicity.
Method: This study employed MTT cell viability assays to investigate the effects of the peptide CB1 agonist RVD and lipid CB1 agonist 2-AG plus the CB1 antagonist AM281 on Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Data was analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Results: RVD (0.01-10μM) had no effect on 10μM Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells, whereas 2-AG (0.02-10μM; P<0.05 vs Aβ 25-35 alone) promoted a concentration dependent inhibition (Figure 1A). The CB1 antagonist AM281 (10μM) had no effect on RVD (10μM) plus 10μM Aβ 25-35, however it abolished the protective effects of 2-AG (10μM; P<0.05 vs Aβ 25-35 alone) on 10μM Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity (Figure 1B).
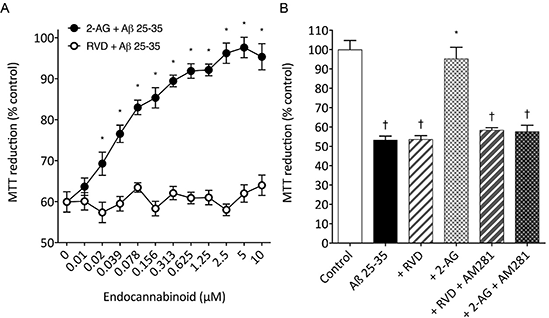
Figure 1. (A) Dose-response curves for RVD plus 10μM Aβ 25-35 and 2-AG plus 10μM Aβ 25-35 on MTT reduction in SH-SY5Y cells. (B) SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to 10μM Aβ 25-35 alone, or plus 10μM RVD alone or 10μM RVD and 10μM AM281 or 10μM 2-AG alone or 10μM 2-AG and 10μM AM281 and cell viability determined by MTT reduction. Results are mean ± SEM (n=8 for each data point); * = P< 0.05 vs Aβ 25-35 alone; † = P<0.05 vs control; (one-way ANOVA).
Conclusion: In conclusion, the peptide cannabinoid RVD is non-protective against Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Lipid based endocannabinoids, such as 2-AG, are protective against Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity1. Our results support the suggestion that endocannabinoid neuroprotection against Aβ involves the intracellular CB1 receptor rather than the extracellular CB1 receptor 5.
References:
(1) Milton NGN (2002). Neurosci Letts 332: 127-130.
(2) van der Stelt M et al. (2006). Cell Mol Life Sci 63: 1410-1424.
(3) Gomes I et al. (2009). FASEB J. 23: 3020-3029.
(4) Ma L et al. (2015) Sci Rep 5: 12440.
(5) Noonan J et al. (2010). J Biol Chem 285: 38543-38554.

