| 030P London, UK 8th European Workshop on Cannabinoid Research |
Effect of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist AM251 on kissorphin protection against amyloid-β neurotoxicity
Introduction: Previous in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate protective properties of kissorphin (KSO) peptides against amyloid-β (Aβ) neurotoxicity1,2. Overexpression of the KiSS-1 gene, that encodes the KSO peptides, is also neuroprotective1,3. Endocannabinoids and KSO peptides are neuroprotective against Aβ 25-35, but not Aβ 31-35 peptides1,4. The KiSS-1 gene expression is regulated by endocannabinoids5. The aim of this study was to determine whether endocannabinoids contribute to KSO protection against Aβ toxicity using a CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist.
Method: This study employed MTT cell viability assays to investigate the effects of the CB1 antagonist AM281 on KSO 1-6 protection against Aβ 25-35 neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. The effects of AM281 on Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in KiSS-1 gene overexpressing SH-SY5Y cells (PKiSS)1,3 was also investigated1,3. Data was analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Results: The CB1 antagonist AM281 (0.01-10μM) promoted a concentration dependent increase in 10μM Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells in the presence of 10μM KSO 1-6 (Figure 1A). The PKiSS protection against 10μM Aβ 25-35 was reversed by the CB1 antagonist AM281 (10μM) and anti-KSO antibody (1μg/ml). In the presence of anti-KSO antibody 10μM 2-AG was protective against 10μM Aβ 25-35.
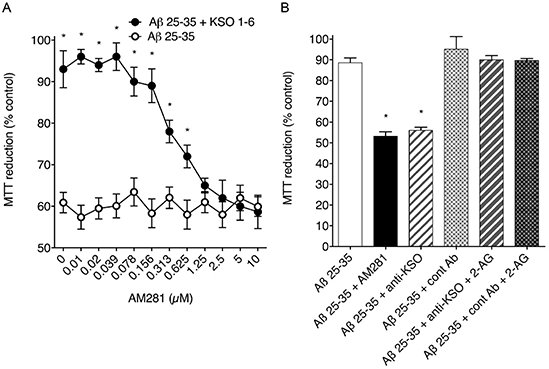
Figure 1. (A) Dose-response curves for AM281 in the presence of 10μM Aβ 25-35 with or without 10μM KSO 1-6, on MTT reduction in SH-SY5Y cells. (B) PKiSS SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to 10μM Aβ 25-35 alone; 10μM Aβ 25-35 plus 10μM AM281; 10μM Aβ 25-35 plus 1μg/ml anti-KSO antibody; 10μM Aβ 25-35 plus 1μg/ml control antibody; 10μM Aβ 25-35 plus 1μg/ml anti-KSO antibody with 10μM 2-AG; 10μM Aβ 25-35 plus 1μg/ml control antibody with 10μM 2-AG; and cell viability determined by MTT reduction. Results are mean ± SEM (n=8 for each data point); * = P< 0.05 vs Aβ 25-35 alone (one-way ANOVA).
Conclusion: In conclusion, protection against Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity by KSO and KiSS-1 overexpression in SH-SY5Y cells is reversed by the AM281 CB1 antagonist. Anti-KSO antibodies prevent neuroprotection by KiSS-1 overexpression and 2-AG restores neuroprotection. This suggests KSO neuroprotection against Aβ involves activation of endocannabinoids.
References:
(1) Milton NGN et al. (2012). ACS Chem Neurosci 3: 706-719.
(2) Jiang JH et al. (2015). Neurobiol Learn Mem. 123: 187-95.
(3) Chilumuri A & Milton NGN (2013). ISRN Neuroscience 2013: 253210.
(4) Milton NGN (2002). Neurosci Letts 332: 127-130.
(5) Karamikheirabad M et al. (2013). Clin Exp Reprod Med 40: 155-162.

