Print version
Search Pub Med
| 043P London, UK Pharmacology 2017 |
The requirement of p38-MAPKinase and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ for the induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by interleukin-4 drives macrophages into an anti-inflammatory phenotype
Introduction: A balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals ensure a homeostatic immune response. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), a nexus between relaying extracellular signals as a mediator of signal transduction, has been associated with pro-inflammatory responses. Growing bodies of evidence have indicated cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and p38 involvement in anti-inflammatory signalling (1); thus, manifesting the complexity of these proteins. Our group has shown COX-2 induction by the anti-inflammatory cytokine, Interleukin-4 (IL-4). The IL-4-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ)-axis is somewhat established (2) and our group showed PPARγ dependent IL-4 induction of COX-2. In the current study, we examined the signalling mechanisms involved in IL-4 induced COX-2 and its effect on macrophage phenotype simultaneously.
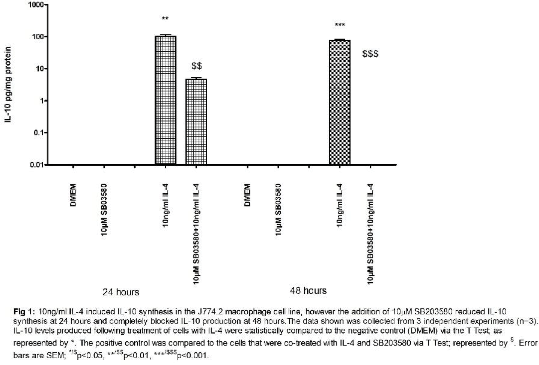
Methods: Macrophage J774.2 cells #<10 were stimulated with 10ng/ml IL-4 for 24 and 48 hours with and without 10μM of the p38 inhibitor, 4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-(4-methylsulfinylphenyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-1H-imidazole (SB203580). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to measure IL-10, the anti-inflammatory cytokine and PGE2, as a measure of COX-2 activity. Furthermore, the effect of SB203580 on IL-4 induced PPARγ activity was measured via a transcription factor activity assay to study the regulation of PPARγ by p38. These experiments were done in parallel with 1μg/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to produce a pro-inflammatory macrophage.
Results: 10ng/ml IL-4 induced IL-10 production at 24 hours (102.48pg/mg protein) and 48 hours (76.68pg/mg protein), however, SB203580, reduced this (4.65pg/mg protein, 0pg/mg protein) (n=3) (fig 1). COX-2 activity was reduced by SB203580 in LPS and IL-4 treated cells at 24 hours and 48 hours respectively. IL-4 induced PPARγ activity by 30 minutes and 48 hours, but this was inhibited by SB203580. Contrarily, LPS inhibited PPARγ activity at 24 and 36-hours; with no effect at any other time points investigated.
Conclusion: IL-4 was able to drive macrophages to produce IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, thus, polarising macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype. IL-10 was produced at 24 hours followed by COX-2 expression at 48 hours, suggesting macrophage polarisation to occur upstream to COX-2 induction. SB203580 reduced IL-10 and PGE2 production at 48 hours, highlighting the dependency of p38 for IL-10 secretion. PPARγ is activated by IL-4 via p38 but is not involved in the LPS pathway, thus entailing its importance in the IL-4 pathway leading to the induction of COX-2. It is evident that p38 regulates PPARγ dependent induction of COX-2 by L-4 in anti-inflammatory macrophages.
References:
1. Jimenez-Garcia L et al. (2015). Eur J Immunol 45: 273-86 2. Szanto A et al. (2010). Immunity 33: 699-712