Print version
Search Pub Med
| 099P London, UK Pharmacology 2017 |
Identification and characterisation of a novel series of quinoxaline-based small molecules as GLP-1R allosteric modulators
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist injectables were proven to be clinically efficacious in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)(1). However, their subcutaneous uses vastly hinder patient compliance, prompting the need for oral GLP-1R agonist therapies(2). Yet, designing GLP-1R small molecule orthosteric ligands is highly challenging(3), leading to a shift in focus onto the search for GLP-1R small molecule allosteric modulators. Several GLP-1R allosteric modulators have been discovered but they are limited by their cytotoxicity(4,5). Thus, the aim of our study was to develop novel GLP-1R small molecule allosteric modulators that could be formulated as novel oral GLP-1R-based therapies.
Method: 6 baits, which are reported GLP-1R agonists, positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) or agonist-positive allosteric modulators, were identified. Ligand-based virtual screening was performed and the baits were screened against 3 chemical libraries, namely e-LEA3D, ZINC and Enamine, that contained over 35 million small molecules, with their 3D shape conformations and electrostatic distributions compared using ROCS and EONs programmes (OpenEye Scientific Software Inc.). 11 drug candidates were identified as a result; they were further tested for their GLP-1R activation and allosteric activities on GLP-1R endogenous ligands, which are GLP-1(7-36)NH2, oxyntomodulin and GLP-1(9-36)NH2 with the use of homogenous TR-FRET LANCE® cAMP detection kit (PerkinElmer®) in Chinese Hamster Ovary-K1 cells stably expressing GLP-1R. All the compounds were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Results: Among the eleven drug candidates, only Compound 11 (N-[3-(cyclopropylamino)quinoxalin-2-yl]benzenesulfonamide), which possesses a quinoxaline ring and a sulfonamide group, potentiated cAMP accumulation mediated by GLP-1(9-36)NH2 by 10-fold (pEC50 values increased from 6.65 ± 0.2 to 7.64 ± 0.3, p<0.01, n>4, Fig. 1). Similar allosteric activities on GLP-1(9-36)NH2 were observed in a series of analogues based on the structure of Compound 11, further confirming the importance of the presence of these two functional groups in the unique allosteric activities observed (Fig. 2).
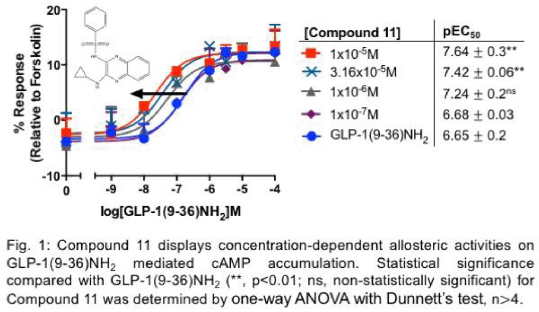
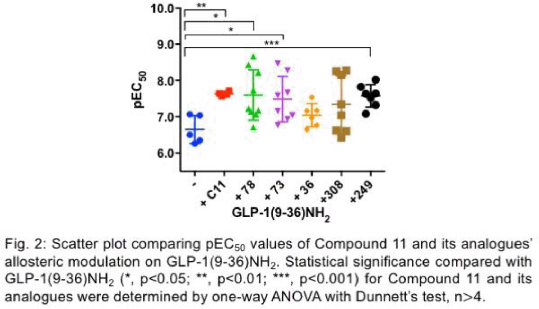
Conclusions: We discovered a novel series of quinoxaline-based small molecules as GLP-1R PAMs that potentiated GLP-1(9-36)NH2 cAMP accumulation. Given the emerging evidence of insulinotropic actions of the widely abundant GLP-1(9-36)NH2, these small molecules can be potentially developed as novel oral GLP-1(9-36)NH2-targeted T2DM treatments.
References
(1) Eng, C. et al. (2014). Lancet 384(9961): 2228-2234.
(2) Defronzo, R. et al. (2015). Nature Reviews 1: 1-23.
(3) Graaf, C et al. (2016). Pharmacological Reviews 68: 954-1013.
(4) Knudsen, L. B. et al. (2007). PNAS 104(3): 937-942.
(5) Sloop, K. et al. (2010). Diabetes 59: 3099-3107.

