| 224P London, UK Pharmacology 2017 |
Effects of the cannabinoid receptor antagonist hemopressin on amyloid-β induced toxicity in mouse Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cells
Introduction: Pepcans are a group of peptide based cannabinoids which are haemoglobin derived. They act as cannabinoid (CB) receptor antagonists/agonists and are found throughout the CNS1. The pepcan hemopressin (Hp) is a nonapeptide antagonist of the CB1 receptor1. Studies have suggested that cannabinoid antagonists, such as the synthetic CB1 antagonist AM251, have memory enhancing activities following brain trauma2. The levels of amyloid-β (Aβ) are elevated during brain trauma and may contribute to tissue damage3. Previous in vitro studies have demonstrated the protective properties of CB1 receptor ligands against Aβ induced neurotoxicity4. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of Hp on Aβ toxicity.
Method: This study employed MTT cell viability assays to investigate the effects of the peptide CB1 antagonist Hp, the peptide CB1 agonist RVD, the lipid CB agonist 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), the synthetic CB agonist O-2545, the synthetic CB1 antagonist AM251, the synthetic CB2 antagonist AM630 plus the synthetic GPR-55 antagonist CID16020046 (10μM for each drug), on 10μM Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in mouse neuroblastoma Neuro-2a (N2a) cells. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Results: Both Hp and 2-AG had a significant protective effect (P<0.05) on Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in N2a cells. The RVD, O-2545 and AM251 had no effect on Aβ 25-35 induced toxicity in N2a cells (Fig 1A). The RVD, AM251, AM630 and CID16020046 had no effect on Hp protection against Aβ 25-35 induced toxicity in N2a cells (Fig 1B).
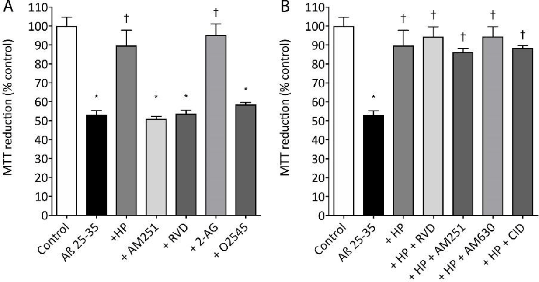
Figure 1. (A) Effect of Aβ 25-35 plus Hp, RVD, 2-AG, O-2545 or AM251 on MTT reduction in N2a cells. (B) Effect of Aβ 25-35 with Hp alone or plus RVD, AM251, AM630 or CID16020046 on MTT reduction in N2a cells. Results are mean ± SEM (n=8 for each data point); * = P< 0.05 vs control; † = P<0.05 vs Aβ 25-35 alone; (one-way ANOVA).
Conclusion: In conclusion, the cannabinoid antagonist Hp is protective against Aβ 25-35 induced neurotoxicity in N2a cells. The Hp protection is not antagonised by RVD or the CB1, CB2 or GRP-55 antagonists suggesting either an action via a non-cannabinoid receptor or that Hp is acting allosterically at an alternate binding site within a CB receptor.
References:
(1) Gomes I et al. (2009). FASEB J. 23: 3020-3029.
(2) Sunada H et al. (2017). J Exp Biol. 220:3026-3038.
(3) Edwards G et al. (2017). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483: 1137-1142.
(4) Milton NGN (2002). Neurosci Letts 332: 127-130.

