| 035P Nottingham, UK 7th Focused Meeting on Cell Signalling |
The human alpha2A-adrenoceptor signals via Gi and Gs proteins.
Introduction: The human alpha2A-adrenoceptor is a Gi-coupled GPCR, thus activation would normally expect to result in a decrease of intracellular cAMP [1]. However, some GPCRs that coupled primarily to Gi-proteins have also been shown to stimulate increases in intracellular cAMP by activating Gs-protein [2-3]. We therefore investigated the signaling of the human alpha2A-adrenoceptor.
Method: CHO cells stably expressing a CRE-SPAP reporter gene (6 cAMP response elements (CRE) upstream of a heat stable secreted placental alkaline phosphatase (SPAP) gene), were secondarily transfected with the human alpha2A-adrenoceptor and a single clone isolated by dilution cloning. Confluent cells were serum starved for 24h, in presence or absence of pertussis toxin (PTX, 100ng/ml) before the addition of ligands (5h, 37°C) and CRE-SPAP production was measured as previously described [2]. Data are shown as mean ± sem of n independent experiments.
Results: Given the primary Gi-signalling of the alpha2A-adrenoecptors, initially, inhibition of 3µM forskolin-stimulated CRE-SPAP production was examined. The concentration response to brimonidine, an alpha2A-adrenoceptor agonist, was best described by two components: at low concentrations, an inhibition of forskolin-stimulated CRE-SPAP production was observed (pIC50 8.98±0.07), followed by a stimulatory component at higher concentrations (pEC50 7.00±0.05, n=15; Figure 1a, Table 1). Yohimbine, an alpha2A-antagonist, caused a similar rightward shift of both components (pKD for yohimbine of 8.45±0.03 for the inhibitory component and 8.65±0.04 for the stimulatory component; n=5, Figure 1a, Table 2), suggesting that both components were occurring via the same receptors. Pre-incubation with PTX completely abolished the inhibition component, suggesting that this component was a Gi-mediated response (Figure 1b, Table 1). The stimulatory response remained and was inhibited by yohimbine to yield a similar pKD (8.31±0.12, n=4). In the absence of forskolin, a stimulation response was observed that was inhibited by yohimbine, once again to yield similar pKD values (Figure 2, Table 2). Brimonidine did not cause any inhibition or stimulation of CRE-SPAP production in the presence or absence of forskolin in the parent CHO-CRE-SPAP cells without the transfected human alpha2A-adrenoceptor (n=3).
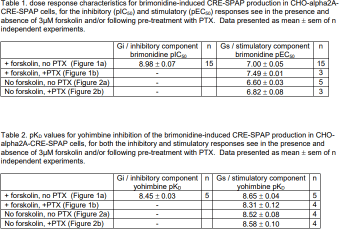
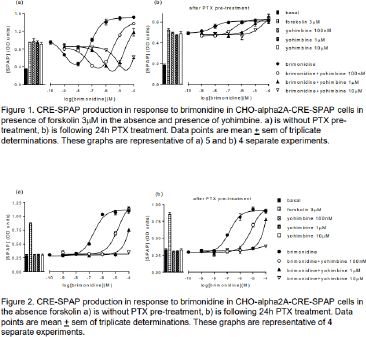
Conclusion: Brimonidine caused a two component CRE-SPAP reporter gene response via the human alpha2A adrenoceptor that is best described as a brimonidine-Gi-mediated inhibitory response at low agonist concentrations followed by a brimonidine-Gs-mediated stimulatory response at higher agonist concentrations.
References:
[1] Ahles A and Engelhardt S (2014). Pharmacol. Rev. 66: 598-637.
[2] Baker JG and Hill SJ (2007). J.Pharm.Exp.Ther. 320:218-228.
[3] Eason MG et al., (1992). J. Biol Chem. 267: 15795-15801.

